2021 Annual Meeting of the ISMRM Iberian Chapter
AUTHORS: Agnès Pérez-Millan, Laia Borrell, José Contador, Mircea Balasa, Albert Lladó, Raquel Sanchez-Valle, Roser Sala-Llonch.
TITLE: Classification between Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia using a single neuroimaging feature.
CONFERENCE: 2021 Annual Meeting of the ISMRM Iberian Chapter
PLACE: Virtual Event
DATES: June 16 - 17, 2021
ABSTRACT:
INTRODUCTION: Alzheimer Disease (AD) and Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD) are common forms of early-onset dementia with different, but partly overlapping, symptoms and brain signatures. There is a need to establish accurate diagnosis and to obtain good markers for prognosis. We combined supervised and unsupervised machine learning (ML) to classify AD and FTD.
METHODS: We included 3T-T1 MRI of 44 healthy controls (CTR, age: 57.8 ± 5.4 years), 53 AD patients (AD, age: 59.4 ± 4.4 years) and 64 FTD patients (FTD, age: 64.4 ± 8.8 years). We obtained subcortical gray matter volumes and cortical thickness (CTh) using FreeSurfer. For ML we performed a principal component analysis (PCA) of all volumes and Cth values. Then, the first principal component (PC) was introduced into a Support Vector Machine (SVM). Overall performance was assessed using k-fold cross-validation.
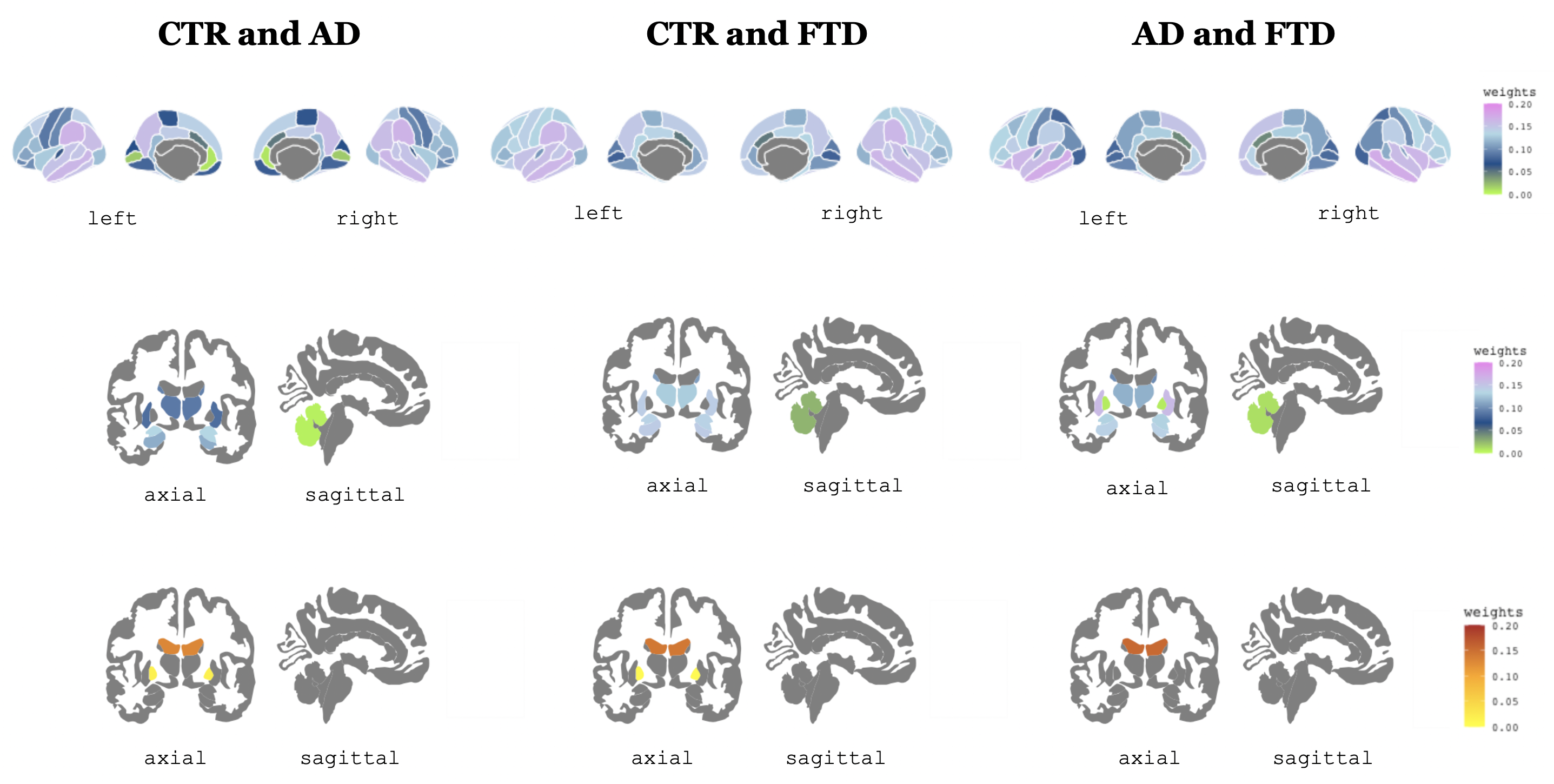
RESULTS: Our algorithm had an accuracy of 85.3 ± 13.6 % in the CTR vs AD classification, 84.2 ± 15.8 % for CTR vs FTD, 67.7 ± 18.5 % for AD vs FTD and 65.8 ± 14.0 % when discriminating the 3 groups. We used the first PC to create disease-specific patterns (Figure 1). Including age in the algorithm led to similar results.
DISCUSSION & CONCLUSION: By using a single feature that combines information from CTh and subcortical volumes, our algorithm is capable to classify CTR, AD and FTD with fairly good accuracy. We suggest that this approach can be used to reduce the amount of data used in ML algorithms while providing interpretable atrophy patterns.